Tercer ventriculostomía endoscópica en la hidrocefalia de presión normal idiopática
Resumen
Introducción: La hidrocefalia de presión normal idiopática es un complejo sintomático caracterizado por afectación de la marcha, incontinencia urinaria y deterioro del estado mental. En la actualidad no existe un esquema diagnóstico estandarizado. La tercer ventriculostomía endoscópica se comenzó a utilizar hace unos años ante la elevada tasa de complicaciones de los sistemas derivativos pero aún no se definen con claridad los factores pronósticos de su éxito y se cuestiona su indicación.
Objetivo: Describir el rol de la tercer ventriculostomía endoscópica en la hidrocefalia de presión normal idiopática.
Métodos: Se realizó la revisión de la literatura en bases de datos PUBMED, además de literatura gris en los servidores de preprints BioRxiv, MedRxiv y preprint.org. Se seleccionaron los artículos de los últimos 15 años sin aplicación de filtros idiomáticos. Se usaron los siguientes descriptores Normal pressure hydrocephalus AND Endoscopic third ventriculostomy. Fueron seleccionados solo aquellos artículos con texto completo disponible.
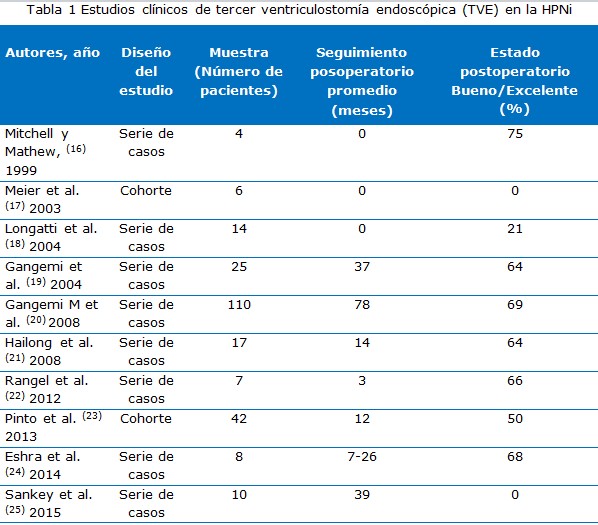
Resultados: Se identificaron un total de 430 artículos. Se analizaron 10 investigaciones sobre tercer ventriculostomía endoscópica en la hidrocefalia de presión normal idiopática, ocho fueron estudios retrospectivos con el 62,5 % de los mismos con una muestra inferior a 15 pacientes, además de dos estudios de cohorte.
Conclusiones: La tercer ventriculostomía endoscópica ha tenido relativo éxito en el tratamiento de pacientes cuidadosamente seleccionados con hidrocefalia de presión normal idiopática. Es un procedimiento seguro y efectivo, encaminado a mejorar la compliance intracraneal a través de la restauración de la pulsatilidad cerebral, y la influencia de la misma en la dinámica del líquido cerebroespinal.
DeCS: HIDROCEFALIA; VENTRICULOSTOMÍA; LITERATURA DE REVISIÓN COMO ASUNTO; TERAPÉUTICA; NEUROENDOSCOPÍA.
Palabras clave
Referencias
Montoya Alan P, Murillo Alvarado K. Diagnóstico de la hidrocefalia de presión normal. Rev Medica Sinerg [Internet]. Mar 2021 [citado 21 Mar 2021];6(3):[aprox. 11 p.]. Disponible en: https://revistamedicasinergia.com/index.php/rms/article/view/654/1164
Fala P, Andronachi V, Gavriliuc M, Gavriliuc P, Andrusca A, Gavriliuc O. NORMAL PRESSURE HYDROCEPHALUS: LITERATURE REVIEW. Arta Médica [Internet]. 2020 [citado 21 Mar 2021];76(3). Disponible en: https://artamedica.md/index.php/artamedica/article/view/49
Nakajima M, Yamada S, Miyajima M, Ishii K, Kuriyama N, Kazui H, et al. Guidelines for Management of Idiopathic Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus (Third Edition): Endorsed by the Japanese Society of Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo) [Internet]. 2021 Feb [citado 15 Ene 2021];61(2):[aprox. 5 p.]. Disponible en: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7905302/.
Macki M, Mahajan A, Shatz R, Air EL, Novikova M, Fakih M, et al. Prevalence of Alternative Diagnoses and Implications for Management in Idiopathic Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus Patients. Neurosurgery [Internet]. 2020 Oct [citado 21 Mar 2021];87(5):[aprox. 9 p.]. Disponible en: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32472677/.
Andersson J, Rosell M, Kockum K, Lilja-Lund O, Söderström L, Laurell K. Prevalence of idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus: A prospective, population-based study. PloS One [Internet]. 2019 [citado 12 Mar 2021]. Disponible en: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6541279/.
Hua R, Liu C, Liu X, Zhu J, Zhang J, Wang L, et al. Predictive Value of Cerebrospinal Fluid Biomarkers for Tap Test Responsiveness in Patients with Suspected Idiopathic Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus. Front Aging Neurosci [Internet]. 2021 [citado 16 Ene 2021];13. Disponible en: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8172576/.
Morel E, Armand S, Assal F, Allali G. Normal pressure hydrocephalus and CSF tap test response: the gait phenotype matters. J Neural Transm [Internet]. 2021 [citado 21 Mar 2021];128(1):[aprox. 5 p.]. Disponible en: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7815574/.
Ryska P, Slezak O, Eklund A, Malm J, Salzer J, Zizka J. Radiological markers of idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus: Relative comparison of their diagnostic performance. J Neurol Sci [Internet]. 2020 Ene [citado 21 Mar 2021]. Disponible en: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31760225/.
Park HY, Kim M, Suh CH, Lee DH, Shim WH, Kim SJ. Diagnostic performance and interobserver agreement of the callosal angle and Evans’ index in idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur Radiol [Internet]. 2021 Jul [citado 21 Mar 2021];31(7):[aprox. 12 p.]. Disponible en: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33409775/.
Andreasen TH, Lilja-Cyron A, Holst AV, Christoffersen D, Johnsen SD, Juhler M. Timing of intraventricular infusion test for diagnosing idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus. Acta Neurochirurgica [Internet]. 2020 [citado 21 Mar 2021];162: [aprox. 7 p.]. Disponible en: https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007%2Fs00701-019-04168-w
Wetzel C, Goertz L, Noé P, von Spreckelsen N, Penner M, Kabbasch C, et al. Flow-regulated versus differential pressure valves for idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus: comparison of overdrainage rates and neurological outcome. Acta Neurochirurgica [Internet]. 2020 [citado 21 Mar 2021]. Disponible en: https://www.springermedizin.de/flow-regulated-versus-differential-pressure-valves-for-idiopathi/17378304
Wang Z, Zhang Y, Hu F, Ding J, Wang X. Pathogenesis and pathophysiology of idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus. CNS Neurosci Ther [Internet]. 2020 Dic [citado 21 Mar 2021];26(12):[aprox. 10 p.]. Disponible en: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7702234/.
Munda M, Spazzapan P, Bosnjak R, Velnar T. Endoscopic third ventriculostomy in obstructive hydrocephalus: A case report and analysis of operative technique. World J Clin Cases [Internet]. 2020 Jul [citado 21 Mar 2021];8(14):[aprox. 10 p.]. Disponible en: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7385605/.
Tasiou A, Brotis AG, Esposito F, Paterakis KN. Endoscopic third ventriculostomy in the treatment of idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus: a review study. Neurosurg Rev. 2016 Oct;39(4):557–563.
Israelsson H, Larsson J, Eklund A, Malm J. Risk factors, comorbidities, quality of life, and complications after surgery in idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus: review of the INPH-CRasH study. Neurosurg Focus [Internet]. 2020 Oct [citado 21 Mar 2021];49(4). Disponible en: https://thejns.org/focus/view/journals/neurosurg-focus/49/4/article-pE8.xml
Mitchell P, Mathew B. Third ventriculostomy in normal pressure hydrocephalus. Br J Neurosurg. 1999 Ago;13(4):382-5.
Meier U, Zeilinger FS, Schönherr B. Endoscopic ventriculostomy versus shunt operation in normal pressure hydrocephalus: diagnostics and indication. Minim Invasive Neurosurg. 2000 Jun;43(2):87-90.
Longatti PL, Fiorindi A, Martinuzzi A. Failure of endoscopic third ventriculostomy in the treatment of idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus. Minim Invasive Neurosurg. 2004 Dic;47(6):342-5.
Gangemi M, Maiuri F, Buonamassa S, Colella G, de Divitiis E. Endoscopic third ventriculostomy in idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus. Neurosurgery [Internet]. 2004 Jul [citado 19 May 2020];55(1):[aprox. 6 p.]. Disponible en: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15214981/.
Gangemi M, Maiuri F, Naddeo M, Godano U, Mascari C, Broggi G, et al. Endoscopic third ventriculostomy in idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus: an Italian multicenter study. Neurosurgery [Internet]. 2008 Jul [citado 19 May 2020];63(1):[aprox. 6 p.]. Disponible en: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/18728569/.
Hailong F, Guangfu H, Haibin T, Hong P, Yong C, Weidong L, et al. Endoscopic third ventriculostomy in the management of communicating hydrocephalus: a preliminary study. J Neurosurg [Internet]. 2008 Nov [citado 19 May 2020];109(5):[aprox. 8 p.]. Disponible en: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/18976086/.
Rangel-Castilla L, Barber S, Zhang YJ. The role of endoscopic third ventriculostomy in the treatment of communicating hydrocephalus. World Neurosurg [Internet]. 2012 Mar-Abr [citado 19 May 2020];77(3):[aprox. 6 p.]. Disponible en: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22120350/.
Pinto FCG, Saad F, Fernandes de Oliveira M, Pereira RM, de Miranda FL, Tornai JB, et al. Role of Endoscopic Third Ventriculostomy and Ventriculoperitoneal Shunt in Idiopathic Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus Preliminary Results of a Randomized Clinical Trial. Neurosurgery [Internet]. 2013 May [citado 19 May 2020];72(5):[aprox. 10 p.]. Disponible en: https://academic.oup.com/neurosurgery/article-abstract/72/5/845/2680608?redirectedFrom=fulltext
Eshra MA. Endoscopic third ventriculostomy in idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus. Alexandria Journal Medicine [Internet]. 2014 [citado 19 May 2020];50(4). Disponible en: https://www.ajol.info/index.php/bafm/article/view/114087
Sankey EW, Jusué-Torres I, Elder BD, Goodwin CR, Batra S, Hoffberger J, et al. Functional gait outcomes for idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus after primary endoscopic third ventriculostomy. J Clin Neurosci [Internet]. 2015 Ago [citado 21 Mar 2021];22(8):1303–1308. Disponible en: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0967586815001186
Alonso Fernández L, Leyva Mastrapa T, Díaz Álvarez M. Factores que influyen en el fallo de la derivación ventrículo-peritoneal en niños y adolescentes con hidrocefalia. Rev cubana neurol neurocir [Internet]. Sep-Dic 2020 [citado 21 Mar 2021];10(3). Disponible en: http://www.revneuro.sld.cu/index.php/neu/article/view/398/614
Fernandes de Oliveira M, Boa Sorte AA, Emerenciano DL, Rotta JM, Mendes GAS, Pinto FCG. Long term follow-up of shunted idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus patients: a single center experience. Acta Neurol Belg. 2021 Dic;121(6):1799-1806.
Lu VM, Kerezoudis P, Patel NP, Jones DT, Cutsforth-Gregory JK, Graff-Radford J, et al. Our Efforts in Understanding Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus: Learning from the 100 Most Cited Articles by Bibliometric Analysis. World Neurosurg. 2020 May;137:429-434.
Fernandes de Oliveira M, Reis RC, Trindade EM, Pinto FCG. Evidences in thetreatment of idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus. Rev Assoc Med Bras [Internet]. 2015 [citado 16 Ene 2021];61(3):[aprox. 5 p.]. Disponible en: https://www.scielo.br/j/ramb/a/4vJMbb7kwY4ZkFF8wKSrGMb/?format=pdf〈=en
Davis A, Luciano M, Moghekar A, Yasar S. Assessing the predictive value of common gait measure for predicting falls in patients presenting with suspected normal pressure hydrocephalus. BMC Neurol [Internet]. 2021 [citado 21 Mar 2021];21:60. Disponible en: https://bmcneurol.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12883-021-02068-0
Alvi MA, Brown D, Yolcu YU, Zreik J, Bydon M, Cutsforth-Gregory JK, et al. Predictors of adverse outcomes and cost after surgical management for idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus: Analyses from a national database. Clin Neurol Neurosurg [Internet]. 2020 Oct [citado 21 Mar 2021];197:106178. Disponible en: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32932217/.
Oertel JMK, Huelser MJM. Predicting the outcome of normal pressure hydrocephalus therapy-where do we stand? Acta Neurochir (Wien) [Internet]. 2021 [citado 21 Mar 2021];163(3):[aprox. 3 p.]. Disponible en: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7886754/.
Enlaces refback
- No hay ningún enlace refback.

Esta obra está bajo una licencia de Creative Commons Reconocimiento-NoComercial 4.0 Internacional.











 La Revista está: Certificada por el CITMA
La Revista está: Certificada por el CITMA Acreditados como: "Web de Interés Sanitario"
Acreditados como: "Web de Interés Sanitario"
